Because data quality is essential, DOMO has been continuously growing its proprietary databases for injection molding simulation and integrated mechanical simulation material data for more than 15 years. This helps engineers to develop parts faster and more reliably.
Materials science and advanced database services
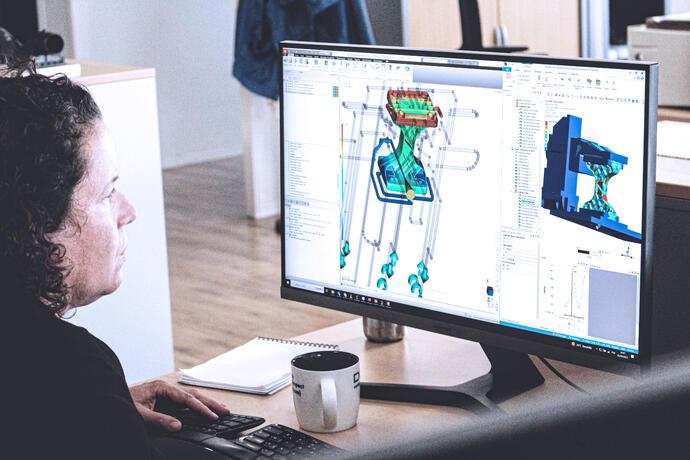

LINKING MATERIALS AND INNOVATION
Key advantages of DOMO's advanced database services
DOMO’s MMI harnesses an extensive database of key property measurements and is powered by Digimat, an advanced material modeling system developed and supported by Hexagon Manufacturing Intelligence. This system offers a wide range of calculations to simulate in-use conditions realistically and predict the performance of injection-molded parts.
What we provide:
- Unique material data on optimized fiber orientation parameters in the Moldflow and Moldex3D public databases with more than 150 injection material cards
- A robust mechanical data meta-modeling approach backed by more than 15 years of scientific experience and collaboration
- A generalized local failure criterion considering the characteristics of the glass-fiber reinforced material
- The largest range of available conditions for reinforced PA material definitions on the market, including for every temperature and humidity condition
- Most advanced material laws on PA6 and PA66 compounds such as for creep or coolant aging
- Leading provider of vibration (NVH), fatigue and thermal dependency Digimat material files
- Predictive simulation with no safety coefficients to consider or over-designing of parts, saving time and money in development costs
- Proof of concept through our demonstrator parts
Material models and measurements

Glass-fiber orientation-based measurements
In the classical approach to generate material data for mechanical simulations, a standard injection molded tensile bar is used. However, this has its limits when it comes to quantifying the anisotropic behavior of glass-fiber reinforced polymers. As only one strong glass-fiber orientation fully aligned with tensile direction is assessed here, the characterized material appears stiffer than in actual parts.
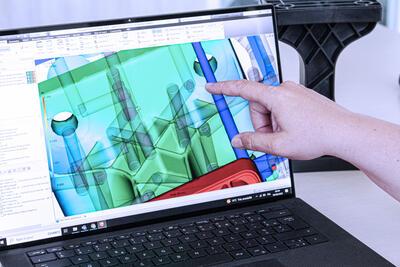
DOMO’s material models for mechanical simulation
Matching material models and mechanical load case is essential for reliable results and to optimize computation time. Thus, the material models for our TECHNYL grades correspond to a variety of load cases. When prediction of local failure is needed, a pseudo-grain-based failure criteria (FPGF) allows detailed insight into the loading of the material and the likelihood of exceeding the glass-fiber orientation-dependent material limits.
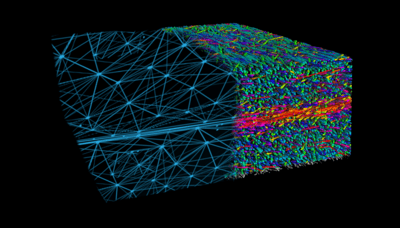
Data for rheological and thermal material models for injection molding simulation
The basis of any injection molding simulation is reliable data. To make sure this high-quality data is available, we take advantage of our in-house physical characterization laboratories, and we collaborate with external partners to characterize our TECHNYL® polyamide materials.
Video: Materials cards for TECHNYL® 4EARTH® recycled solutions
DOMO has created no less than 700 models for its TECHNYL® 4EARTH® A4E 218 grades in Digimat, so that engineers can evaluate the performance of parts by embedding a material model within their standard Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) tools. TECHNYL® 4EARTH® A4E 218 grades are heat-stabilized 100% recycled PA66, reinforced respectively with 30%, 35% and 50% glass fibre. This vast range of models enables customers to perform integrative simulations covering an exhaustive array of environmental conditions and load cases. Additionally, lifecycle analysis (LCA) of the product is also available.
Alexandre Chatelain, Simulation Models Database Manager at DOMO, provides more insights:

Contact us
MMI helps manufacturers understand the real behavior of materials before moving forward with physical production phases. Contact us now for more information.